What Are Neurons: How Brain Messages Travel
The human brain is one of the most complex organs in nature. It allows us to think, move, feel, and remember. But how does the brain actually send and receive messages? The answer lies in tiny but powerful cells called neurons. These cells act as messengers of the nervous system, carrying signals between different parts of the body and the brain. Without neurons, we would not be able to move a finger, speak a word, or even sense the world around us.
In this article, we will explain what neurons are, how they work, and how brain messages travel through them in simple terms.
What Are Neurons
Neurons are specialized cells in the nervous system that transmit information through electrical and chemical signals. Unlike most other cells in the body, neurons are designed to send rapid messages across long distances. They form networks that connect the brain, spinal cord, and body, allowing us to react to our environment in real time.
An average human brain contains around 86 billion neurons. Each neuron can connect with thousands of other neurons, forming trillions of connections. This network is what gives the brain its incredible power and flexibility.
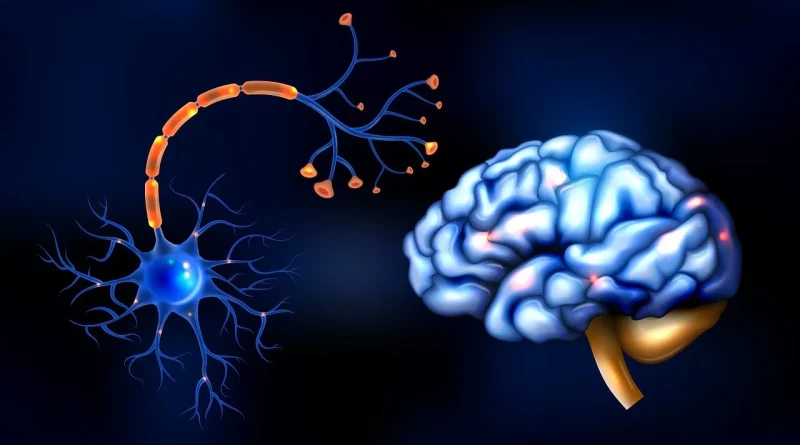
Structure of a Neuron
To understand how neurons work, it helps to know their structure. Although neurons come in different shapes and sizes, they all share three main parts.
Cell body (soma) – This is the control center of the neuron. It contains the nucleus, which holds the DNA, and other parts that keep the cell alive and working.
Dendrites – These are tree-like branches that receive signals from other neurons. The more dendrites a neuron has, the more information it can collect.
Axon – This is a long, thin fiber that carries messages away from the cell body toward other neurons, muscles, or glands. Some axons can be very short, while others, like those in the spinal cord, can be over a meter long.
At the end of the axon are terminals that release chemicals to pass the message to the next neuron. Many axons are covered with a fatty layer called the myelin sheath, which speeds up the signal and protects the axon.
How Do Neurons Send Messages
Neurons send messages in two main ways: electrical signals and chemical signals.
Electrical signals occur inside the neuron. When a neuron is stimulated, an electrical impulse called an action potential travels down the axon. This impulse is very fast, moving in milliseconds.
Chemical signals occur between neurons. When the electrical impulse reaches the axon terminals, it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters cross a tiny gap called the synapse and bind to receptors on the next neuron. This chemical connection starts a new electrical impulse in the receiving neuron.
Together, these electrical and chemical steps allow neurons to communicate across the brain and body.
The Journey of a Brain Message
To better understand the process, imagine you touch a hot stove. Sensory neurons in your skin detect the heat and send electrical signals through their axons to the spinal cord and brain. The brain processes the information and sends a command through motor neurons to your hand muscles, making you quickly pull back.
This entire process happens in a fraction of a second. Neurons are so efficient that they allow the body to react almost instantly to danger.
Types of Neurons
Not all neurons have the same job. There are three main types of neurons that work together to keep the body functioning.
Sensory neurons – These neurons carry information from the senses to the brain. For example, they help you see, hear, smell, taste, and feel.
Motor neurons – These neurons carry instructions from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands, allowing movement and actions.
Interneurons – These neurons connect sensory and motor neurons within the brain and spinal cord. They are responsible for processing information and decision-making.
Together, these three types of neurons create a communication system that links the brain with every part of the body.
Why Neurons Are Important
Neurons are essential for every action we take. They control voluntary movements like walking and talking, as well as involuntary actions like breathing and heartbeat. Neurons also form the basis of memory, emotions, and thought.
When neurons are damaged or fail to communicate properly, it can lead to serious health problems. Conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and epilepsy are linked to neuron function. This is why studying neurons is one of the most important areas of medical research.
How Fast Do Neurons Work
Neurons are extremely fast messengers. Some signals travel at speeds of up to 120 meters per second. This speed allows the body to respond quickly to external stimuli, like catching a ball or avoiding danger. The speed depends on the type of neuron and whether it has a myelin sheath, which boosts conduction.
Neurons and Learning
One of the most fascinating things about neurons is their ability to change. The brain can form new connections between neurons in response to learning and experience. This is known as neuroplasticity. For example, when you learn a new skill, your neurons strengthen their connections and sometimes even create new pathways. This flexibility allows humans to adapt to new situations and challenges throughout life.
Protecting Neurons and Brain Health
Because neurons are so critical, protecting brain health is essential. Unlike many other cells in the body, neurons do not easily regenerate if damaged. Here are some simple steps to keep neurons healthy.
Eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants
Exercise regularly to improve blood flow to the brain
Get enough sleep, which is vital for memory and neuron repair
Stay mentally active with reading, puzzles, or learning new skills
Avoid smoking, drugs, and excessive alcohol, which can harm neurons
Manage stress, as chronic stress can damage connections between neurons
Conclusion
Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system and the reason our brains can send messages throughout the body. By using electrical impulses and chemical signals, they allow us to think, move, sense, and feel. With billions of neurons forming countless connections, the brain is one of the most powerful systems in the natural world.
Understanding neurons not only explains how brain messages travel but also highlights the importance of keeping our brains healthy. Protecting neurons through good habits ensures that our minds and bodies continue to function at their best.